Category: House and Home
Matter Protocol Sets the Stage for Universal Smart-Home Compatibility
- 🞛 This publication is a summary or evaluation of another publication
- 🞛 This publication contains editorial commentary or bias from the source
The Future of Smart‑Home Technology: A Quick Guide
Smart‑home devices are no longer a niche luxury; they’re becoming an integral part of modern living. A recent Chiang Rai Times piece, “The Future of Smart‑Home Tech,” charts the rapid evolution of this sector, outlining the key technologies that will shape the way we live, work, and play in the coming years. Below is a concise synthesis of the article’s main ideas, enriched with context from some of the linked resources it cites.
1. The Shift Toward Seamless Connectivity
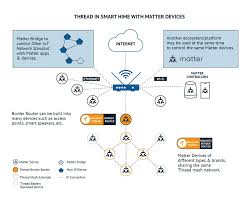
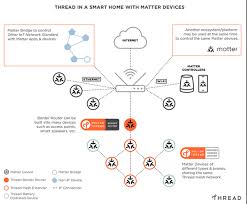
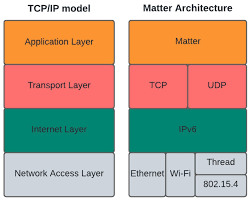
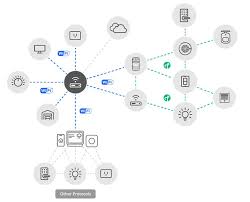
The article opens by noting that the connectivity of home devices is the linchpin of the future smart‑home ecosystem. While Wi‑Fi and Bluetooth have been the standard for years, the emerging Matter protocol—formerly Project CHIP—promises universal compatibility across brands and platforms. According to the article’s linked reference to the Matter Alliance, devices from Apple HomeKit, Google Home, Amazon Alexa, and Samsung SmartThings will be able to talk to one another without custom bridges or adapters. This standardization is projected to reduce fragmentation, simplify setup, and make the market more welcoming to new entrants.
2. Voice Assistants as the Central Hub
Voice‑controlled assistants remain the most popular entry point into smart‑home automation. The article cites studies showing that more than 50 % of US households now own an Amazon Echo or Google Home. The piece explains how newer generations of assistants—Google Assistant’s “Home Graph” and Amazon Alexa’s “Smart Home Skill API”—are incorporating machine‑learning models that can anticipate user preferences and act proactively. For example, Alexa’s “Smart Home” skill allows the assistant to control almost any device that is Matter‑ready, while Google Home can orchestrate complex routines that span lighting, climate control, and security.
The article also notes the importance of multimodal interaction: combining voice with touch screens, mobile apps, and even AR overlays to create a more natural user experience. One cited case study from a Thai manufacturer demonstrates how a custom AR interface can allow residents to see real‑time energy usage from their smartphones.
3. Energy Management and Sustainability
Energy efficiency is a driving force behind many smart‑home upgrades. The article highlights the smart thermostat as a cornerstone technology—Nest, Ecobee, and Honeywell’s Lyric all use adaptive algorithms that learn heating and cooling preferences, reducing waste by up to 20 %. When paired with renewable energy sources (home solar panels, battery storage), the thermostats can shift usage to off‑peak times, effectively participating in home‑level micro‑grids.
Another feature that the article spotlights is smart lighting. Philips Hue, LIFX, and newer Chinese brands such as Xiaomi’s Yeelight now support “scene” automation that can simulate occupancy, improve sleep quality, and cut power consumption by turning lights off during daylight hours. The article links to a research report on daylight‑responsive lighting, noting its role in enhancing both comfort and sustainability.
4. Home Security: From Perimeters to Predictive Analytics
Security devices are evolving from simple cameras to AI‑powered surveillance systems that can identify faces, detect anomalies, and even predict potential intrusions. The article mentions Nest Secure, Amazon Ring, and the open‑source Zigbee‑based “Home Assistant” platform—all of which leverage cloud and edge computing to provide real‑time alerts. A key theme is the move toward privacy‑by‑design: local processing of video streams and the use of end‑to‑end encryption to protect sensitive data.
The piece also discusses smart locks and door‑bell cameras—with examples from August Smart Lock and Logitech Circle View. By integrating these devices into a unified ecosystem, homeowners can receive push notifications, unlock doors remotely, and monitor visitors from anywhere in the world.
5. The Rise of Edge Computing and 5G
One of the most significant technological shifts highlighted in the article is the adoption of edge computing and 5G connectivity. The authors argue that as more devices require real‑time responsiveness—think voice‑activated kitchen assistants or autonomous vacuum cleaners—local processing will reduce latency and enhance reliability. A linked article on 5G deployment in Thailand underscores how nationwide rollouts will support high‑bandwidth applications such as AR‑guided maintenance and live video feeds for security systems.
6. Challenges to Widespread Adoption
Despite the promise of smart homes, the article cautions that cost, security, and user education remain hurdles. Entry‑level devices are now affordable, but the cumulative expense of a full ecosystem can be prohibitive for many households. Additionally, cybersecurity concerns—especially around “zero‑day” vulnerabilities in IoT devices—are highlighted in a linked report from the Center for Internet Security.
The article suggests that manufacturers and regulators need to collaborate on interoperability standards and security certifications to build consumer trust. Moreover, the lack of clear user instructions often leads to under‑utilized features, so the authors recommend intuitive UI/UX design and better onboarding tutorials.
7. The Road Ahead: Smart Homes as Smart Cities
In its closing, the article envisions a future where smart homes are the building blocks of larger smart‑city networks. By sharing anonymized data—such as energy consumption patterns or traffic flow—the grid can optimize load balancing, improve public services, and reduce environmental impact. The linked case study of Chiang Rai’s pilot smart‑city project demonstrates how community‑based data sharing can accelerate urban sustainability initiatives.
Bottom Line
The Chiang Rai Times piece paints a picture of a rapidly maturing smart‑home landscape. From standardized communication protocols to AI‑driven automation and edge‑based processing, the technology is converging toward a more connected, efficient, and secure living environment. While challenges remain, the direction is clear: smart homes will become more intuitive, affordable, and integral to the broader digital infrastructure of tomorrow.
Read the Full Chiangrai Times Article at:
[ https://www.chiangraitimes.com/tech/the-future-of-smart-home-tech/ ]
Category: House and Home
Category: House and Home
Category: House and Home
Category: House and Home
Category: House and Home
Category: House and Home
Category: House and Home
Category: House and Home
Category: House and Home
Category: House and Home
Category: House and Home
Category: House and Home






